
When developing a project schedule, especially in the context of the Project Management Professional (PMP) exam, the initial focus is often on determining who is responsible for each task and identifying dependencies among the activities. However, as the planning progresses, it becomes evident that some team members are overloaded with work while others have less on their plates. To address this imbalance, a process called resource optimization is implemented. Resource optimization aims to optimize the allocation of resources, including human and material resources, to the project activities. In this article, we will explore two important techniques used in resource optimization: Resource Leveling and Resource Smoothing.
Resource leveling is a project management technique used to balance the workload of team members by distributing work evenly across the project duration. It achieves this by making adjustments to the start and finish dates of activities, taking into account resource constraints, availability, and activity dependencies.
So it is a technique which ensures that no individual is overloaded beyond their capacity, leading to more efficient and effective project execution. Resource Levelling is applicable to both human and material resources. It is needed when:
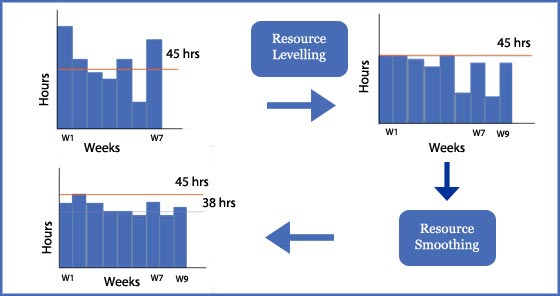
Like when a resource is assigned to multiple activities simultaneously, resulting in over-allocation. A resource cannot work beyond 8 hours in a day. So 8 hours is a constraint that needs to be considered. As a result, it may bring a big change in the project schedule because we have to level it. For example, you do not have more than 45 hours a week in your schedule. Applying this resource constraint may result in a change in the project schedule and its duration. When we apply 45 hours constraint to a 7-week project, then it may become a 9-week project schedule.
Resource Constraints drive Resource Leveling.
Now, the question arises: how do we identify resource constraints? The network diagram is a primary source for detecting these constraints. When creating a network diagram, the focus is primarily on capturing dependencies (mandatory or discretionary) between activities. Resource constraints become apparent when assigning resources to these activities. It is important to note that resource levelling has the potential to alter the critical path of the network diagram due to changes in the project schedule’s duration. The impact on the critical path is an intriguing aspect of this process.
Let’s consider an example using the Critical Path Method (CPM). Suppose we have three activities: A, B, and C, each requiring eight work hours. Initially, we assigned Raj to Activities A and B and David to Activity C. We plan for Activity A to start on day one, followed by Activity B, and then Activity C, with the project ending on day two. However, upon examining the resource allocation, we discovered Raj is overloaded, working 16 hours on day one. To resolve this, we modify the schedule by making activities A, B, and C sequential, resulting in a project duration of three days. By doing so, we limit Raj’s workload to eight hours daily, adhering to the resource constraints.
Resource leveling provides numerous advantages. Firstly, it addresses inefficient resource allocation, optimizing the utilization of available resources. By leveling the workload, it ensures a balanced distribution of tasks, preventing overloading or underutilization of resources. Secondly, resource leveling improves project visibility and control by highlighting resource constraints and their impact on the project schedule. This enables better decision-making and resource management throughout the project. Lastly, resource leveling minimizes conflicts and bottlenecks, fostering collaboration and smoother project execution. Overall, resource leveling enhances project efficiency, productivity, and the likelihood of successful project completion.
Resource levelling does come with certain disadvantages that need to be acknowledged. Resource Leveling to take care of constraints can lead to task delays. It’s important to recognize these limitations and find strategies to mitigate their impact on project timelines and resource utilization.
Resource smoothing is a technique used in project management to optimize resource allocation without extending project duration. It adjusts the activities of a schedule after resource leveling to ensure resource requirements stay within predefined limits. The focus is on achieving a balanced workload by utilizing available slack in the schedule. Through strategic adjustments within the flexible areas of the schedule, resource smoothing aims to refine allocation for improved work efficiency.
The purpose of resource smoothing is to create a more even distribution of resource usage over time. While resource leveling balances the workload across the project duration, resource smoothing focuses on maintaining a manageable and realistic workload by considering factors such as breaks, non-project work, or other project-related responsibilities. It recognizes that assigning activities for the full 8 hours each day may not always be practical or efficient. By implementing resource smoothing, project managers can fine-tune the allocation of resources, providing some flexibility in scheduling daily activities while still meeting project requirements. It aims to optimize resource utilization and create a more efficient and manageable project plan.
Continuing with the Resource Leveling example, where the original 7-week schedule was extended to 9 weeks to accommodate the maximum available time of 45 hours, further optimization is required to achieve the desired allocation of 38 hours per week. The purpose of resource smoothing is to distribute the workload in a way that comes closer to this desired allocation. During the resource smoothing process, adjustments are made to the project schedule by leveraging available slack or flexibility. This means that resource smoothing focuses on optimizing resource utilization within the existing timeframe of the project. By utilizing free and total float, project managers can make strategic adjustments to activities, allowing for a smoother distribution of resources and minimizing overloading. This technique helps ensure a more balanced workload and enhances resource efficiency, contributing to preventing stressed execution of the project.
Resource smoothing requires available slack for optimal resource allocation.
As we are not aiming to change the project duration, it does not affect the critical path; we smoothed the project schedule by playing around with the free and total float. However, it is important to note that complete smoothing may not always be feasible, as there will be instances where team members must work their maximum allocated hours due to project constraints.
Resource smoothing in project management optimizes resource allocation within predefined limits, promoting efficient resource utilization and balanced workloads. By strategically adjusting activities and utilizing available slack, enhances productivity and ensures a healthier work-life balance for team members.
A potential limitation of resource smoothing is its dependency on the availability of slack in the project schedule. If there is insufficient slack, it can be challenging to achieve the desired resource allocation through smoothing. In such cases, resource smoothing may not be feasible.
The following diagram illustrates and summarizes the sequence of Resource Leveling followed by Resource Smoothing. In the Resource Leveling phase, the work is evenly distributed among the available resources, resulting in an extension of the project duration from 7 weeks to 9 weeks. This ensures that no resource is overloaded beyond its capacity. Subsequently, the Resource Smoothing technique is applied to achieve the desired level of resource allocation. Instead of allocating 45 hours of work per week, the allocation is adjusted to 38 hours per week. This allocation allows for a more balanced workload and provides some breathing space for the resources involved. Overall, this combined approach of Resource Leveling and Resource Smoothing optimizes resource utilization and helps in maintaining a more manageable project schedule.
| Resource Levelling | Resource Smoothing |
| Applies resource constraints, potentially altering the duration. Adjusts dates to avoid overloading and enhance efficiency within the defined resource limitations. | It is applied after Resource Leveling, as it requires accommodating the resource constraints first. In resource smoothing, slack is utilized to optimize resource allocation without further changing the project duration, as the total allocation of a specific resource remains unchanged. |
| Resource Leveling is primarily driven by resource constraints like you do not have more than 45 hours of the given resource for a week. | Resource smoothing is primarily concerned with achieving desired resource allocation limits. For example, if we have 45 hours available for a specific resource, but we prefer to allocate only 38 hours per week, this allows us to ensure a more manageable workload. |
| In resource leveling, the identified allocation limits must be strictly enforced and applied to the project schedule. This means that the assigned resources cannot exceed the predefined limits, ensuring that the workload is distributed within the specified constraints. | Resource smoothing optimizes resource allocation within float boundaries, considering desired limits. However, if there is insufficient slack, achieving the desired limits may not always be possible. |
| When applying resource leveling, project dates may be adjusted, potentially impacting the critical path due to the influence of resource constraints. | Resource smoothing will not change the critical path; it tries to make the best use of slack. |
In Agile iterations, teams naturally manage the distribution of work, akin to resource leveling, by leveraging their capacity and velocity. During the iteration planning meeting, the team evaluates how much work can be accomplished within the defined time frame and take work from the top of the product backlog. Through self-organization, the team collaboratively determines how to allocate the iteration backlog items, ensuring an even distribution of tasks and resources. This organic approach aligns with the principles of resource smoothing, as the team strives to work within desired limits while maximizing their productivity.
Additionally, the concept of elapsed time in estimation plays a crucial role in resource optimization. When estimating tasks or user stories, teams consider the elapsed time it takes for an activity to be completed, accounting for factors such as waiting time, dependencies, and potential delays. By factoring in elapsed time during estimation, teams gain a more realistic understanding of the actual duration required to complete a task. This helps in resource optimization by enabling better allocation of resources and workload distribution. Teams can identify potential bottlenecks or resource constraints, adjust their plans accordingly, and ensure that resources are effectively utilized over time.
So, by combining the principles of resource leveling, resource smoothing, and considering elapsed time in estimation, Agile teams can effectively balance workloads, optimize resource utilization, and enhance their ability to meet project deadlines. This holistic approach fosters efficient and collaborative project execution, ultimately leading to successful outcomes.
Resource Leveling and Resource Smoothing are two valuable techniques used in project management to balance workloads and optimize resource allocation. Resource leveling focuses on adjusting the project schedule to distribute work evenly, considering resource constraints and dependencies among activities. It aims to prevent the overloading of individuals and achieve a more efficient project execution. On the other hand, resource smoothing aims to achieve a desired level of resource allocation per week, utilizing available slack while maintaining the project duration. Both techniques play a crucial role in managing resources effectively and ensuring project success. By understanding their differences and when to apply each technique, project managers can make informed decisions to optimize resource utilization and deliver projects on time and within constraints.
I’m sure I have answered all your questions on the differences between resource leveling and resource smoothing. You may also like to watch a video presentation on the differences between resource leveling and resource smoothing.
If you have aspirations to pursue the PMP certification, enroll with us for comprehensive support in your PMP certification journey. We offer expert guidance in exam preparation, assistance with the application process, and help in scheduling the exam. With our assistance, you can confidently navigate the certification process and increase your chances of success.
iZenBridge offers a wide range of comprehensive FREE resources to support you throughout your PMP certification journey. Explore our PMP Free Practice test, which provides a realistic simulation of the actual exam and helps you assess your preparedness with up-to-date questions. Our 50 Agile PMP Questions tutorial also delves deep into essential PMP Agile concepts, such as working with Requirements, value delivery, Agile Metrics, incremental delivery, and feedback. These tutorials provide detailed explanations and expose you to common Agile-related PMP exam questions. Whether you’re new to Agile or seeking to strengthen your understanding, our scenario-based PMP Agile questions are valuable tools for effective concept comprehension.
| Name | Date | Place | – |
| PMP Certification and Training | 17 July – 15 Aug 2025 | Bangalore | More Details |