
The essence of successful collaboration lies in team members understanding what is expected of them, as well as knowing what they can expect from their colleagues. In project management, various tools are employed to achieve this clarity, with the RACI matrix (or chart) being one of the most frequently utilized.
The RACI chart, also known as the RACI matrix, is a highly popular tool among project managers, as it effectively delineates roles and responsibilities. By presenting a comprehensive overview of various roles on a single page, the RACI matrix fosters improved communication and understanding within the team.
The RACI matrix, alternatively referred to as a RACI chart, serves as an indispensable responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) in the field of project management. Fundamentally, it consists of a straightforward and well-organized spreadsheet or table that arranges all stakeholders or project roles in columns, with high-level project tasks or activities presented as rows. To complete the matrix, each stakeholder’s or project role’s level of involvement in every task is assessed, utilizing the letters R, A, C, or I to denote their distinct roles.
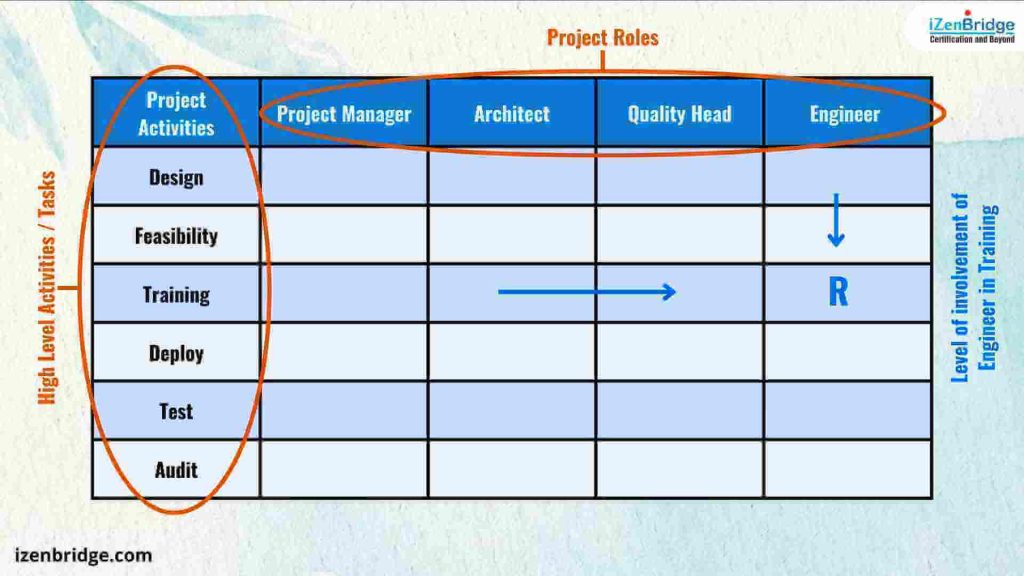
R, A, C, I represent:
Each designation is explained as follows:
The responsible designation signifies that a task is explicitly assigned to a specific role or individual. In simple terms, having responsibility for a given task means that the person or role is in charge of ensuring its completion. It is essential to have at least one individual responsible for each task; otherwise, no one will get it done. Additionally, it is possible to have multiple people responsible for the same task, meaning that for a task row, more than one person can be designated as responsible.
Typically, responsible individuals are part of the project team and frequently serve as developers or creators.
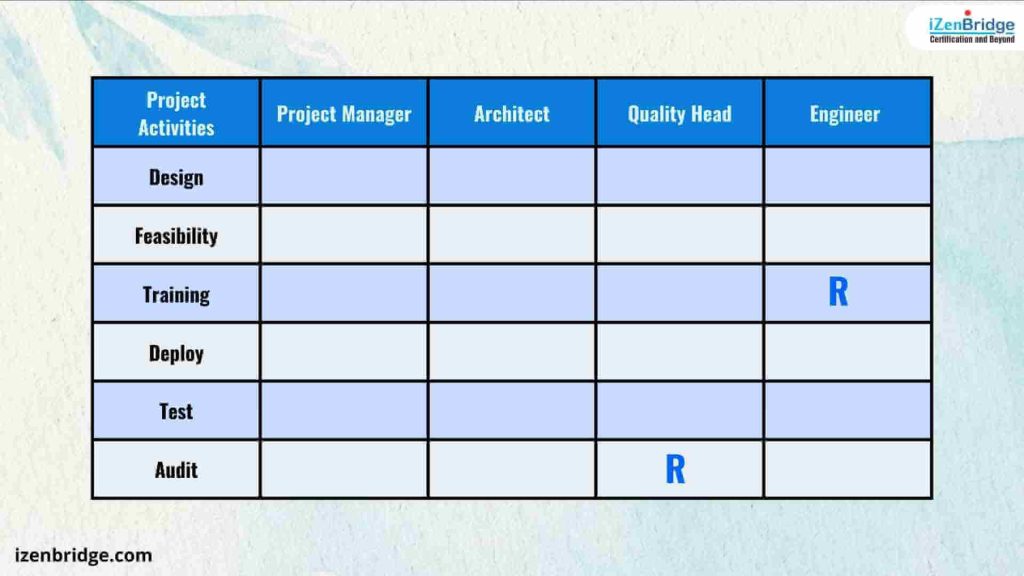
In this illustration, the engineer is responsible for conducting training, meaning they will carry out the training session. Meanwhile, the Quality Head is responsible for conducting audits, signifying that they will perform the audit tasks.
In the RACI model, the accountable person is someone who is held accountable for ensuring the completion of an activity. While this individual may not directly perform the task, they oversee its execution and are answerable to other stakeholders if anything goes awry. The accountable role involves ensuring that the person or team assigned to a task understands the project’s expectations and adheres to deadlines. Traditional projects tend to emphasize a single point of accountability, meaning each task should have only one accountable person. However, more collaborative approaches may also allow for shared accountability for specific activities.
Accountable individuals generally occupy leadership or management positions within the project team.
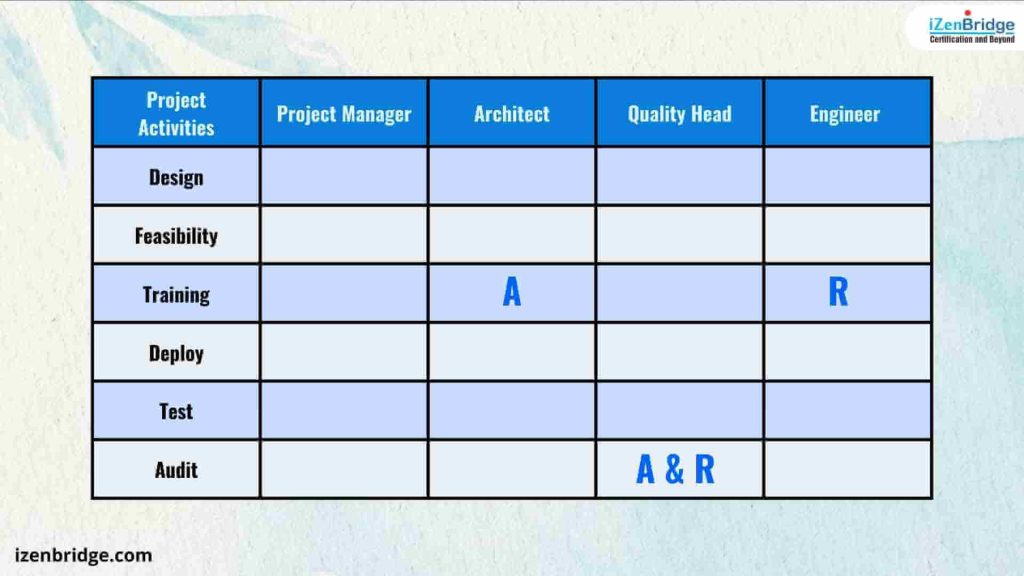
In this example, the engineer is responsible for conducting training, while the architect is accountable for the training activity, ensuring that the training achieves its objectives and that the engineer completes it on time. Simultaneously, the Quality Head holds both responsibility and accountability for conducting audits, indicating that they will not only perform the audit tasks but also be answerable for the audit’s quality and timely completion.
While performing work, individuals may need to consult others for advice, discussing design options, or seeking guidance. The ‘Consulted’ designation in the RACI matrix indicates which stakeholders should be consulted for a specific task or activity. These consulted stakeholders provide valuable input and feedback on the project’s progress. When creating the RACI matrix, project managers should identify all potential stakeholders and include an appropriate number of consulted parties.
Consulted parties may encompass project team members whose work is influenced by the outcome, as well as colleagues from other teams or departments.
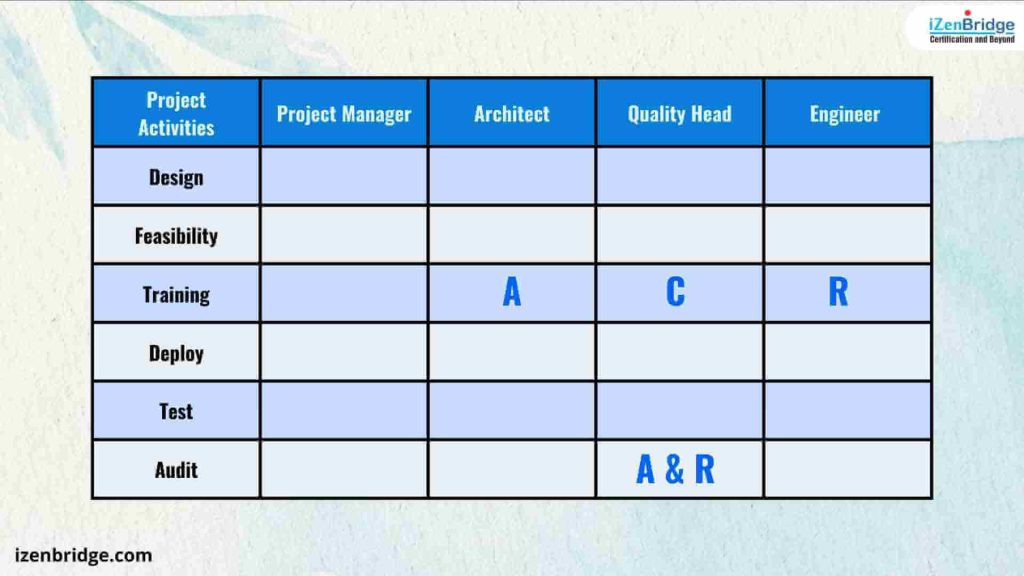
In this example, when the architect and engineer are planning the training activity, they should consult with the Quality Head to ensure that any concerns related to quality are addressed and incorporated into the training.
Informed individuals are those who need to stay apprised of ongoing developments, as their tasks may be affected by the project’s progress. While they generally do not offer advice or make decisions related to a specific task, it is essential to keep them informed due to the potential impact on their work.
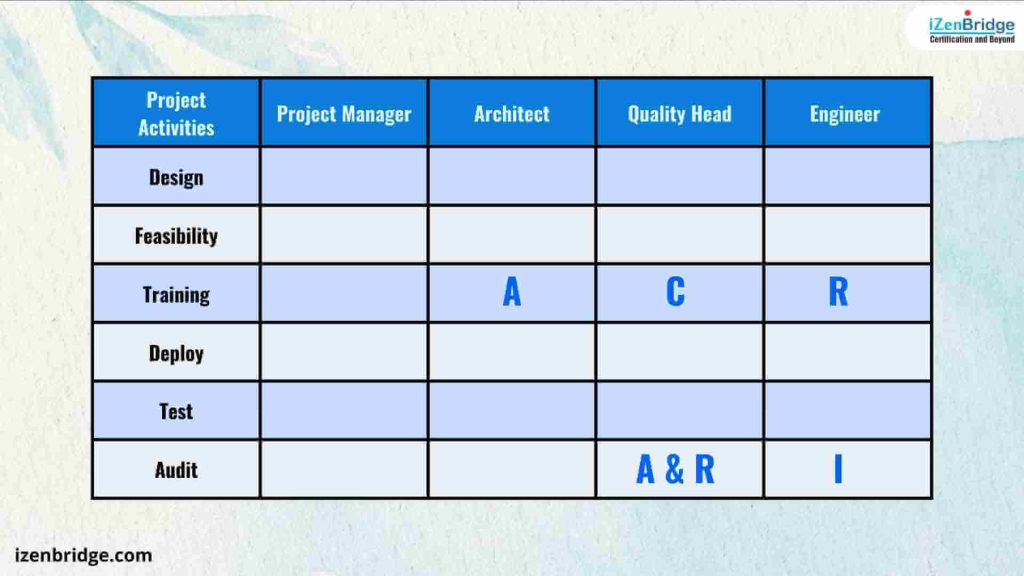
In this example, the engineer is designated as ‘Informed’ for the audit activity. While the Quality Head is conducting the audit, there is an agreement in place to ensure that information regarding the audit is shared with the engineer as it unfolds.
Upon gaining an understanding of the RACI chart, you may envision numerous ways to utilize it for managing your projects. In fact, it can be employed in any context where clarifying roles and responsibilities is essential. The RACI chart serves as a high-level tool to define roles and responsibilities, but it does not replace project scheduling activities that involve assigning specific tasks or activities to team members. Instead, it can function as a guiding tool for project scheduling.
RACI can be incorporated into various aspects of project management:
As we know, approximately 50% of PMP exam questions are based on agile approach. Generally, RACI is not as prevalent in agile approaches since they have clearly defined roles and emphasize more collaboration and shared accountability within the project team.
However, when employing a hybrid approach, clear communication with other project teams and systematic clarification of roles and responsibilities is crucial. In this context, the RACI chart can be a valuable tool. When using hybrid approaches, it is essential to apply RACI to delineate roles and responsibilities. For adaptive projects, it is important to encourage collaboration in determining who is responsible for each task.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the RACI matrix is an invaluable tool in project management, fostering clear communication and collaboration within teams by providing a comprehensive overview of roles and responsibilities. By incorporating the RACI matrix into various aspects of project management, you can ensure that your team stays focused, engaged, and aligned with the project’s objectives.
As you prepare for the PMP exam, keep in mind the tips and insights provided in this article to help you better understand the RACI matrix and its application in various project scenarios. Remember, the key to successful project management lies in effective communication and a thorough understanding of the roles and responsibilities of all team members.
If you are eager to enhance your project management skills and achieve PMP certification, we invite you to enroll in our PMP Preparation program. Our comprehensive program will provide you with the knowledge and tools needed to navigate the complex world of project management and successfully complete the certification process. Don’t miss this opportunity to advance your career and become a certified project management professional. Enroll now and take the first step towards your PMP certification!
| Name | Date | Place | – |
| PMP Certification and Training | 17 July – 15 Aug 2025 | Bangalore | More Details |